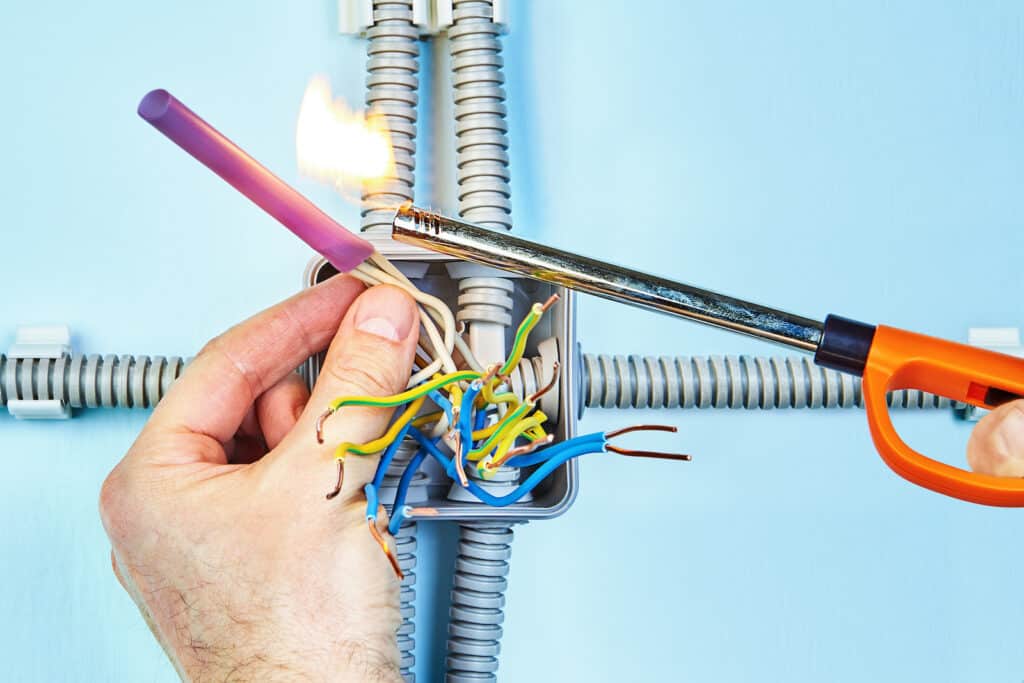
Human Electricity — Why Cables Need to Be Insulated
The human body—because it is made out of atoms (including protons and electrons) is a good conductor. This is why it is ill-advised to take a hairdryer into the bathtub with you or stick your fork into a toaster. That’s because the electrical charge inside the outlet or the toaster will ‘transfer’ into the metal (another good conductor) and then ‘transfer’ it into your hand resulting in the very recognizable zing. The human heart runs on tiny electrical impulses that allow for the chambers of this thick muscle to contract. Tiny electrical currents also power our muscles and allow us to create action potentials that convert into movement. Electrical cables need insulation to keep that energy from wandering into other good conductors. So in order to shield or protect the electrical current running through cables, a certain material free of wandering electrons is needed. That’s when heat shrink tubing comes in.
Electronics Advancement During the Cold War
Like any conflict between two nations or powers, the Cold War involved rapid advancements in various kinds of technology. During this time, the United States and the former Soviet Union competed in almost every area of society. From the space race to weapons, to military advancements the two nations competed with each other ferociously. A lot of this was all with the intent of reaching breakthroughs in atomic energy. The Manhattan Project had spearheaded this effort in the 1940s and produced the world’s first atomic bomb that brought the Second World War to a halt. One area in which the two nations fought was in the area of communications and electrical systems. During this time, a chemical engineer named Paul Cook experimented with polymers and cross-linking. Cross-linking is a type of chemical reaction between polymer chains. As these polymers link together it changes the chemical properties. This little discovery was to be necessary for the development of heat shrink tubing. Cook’s company — named Raychem Corporation — successfully applied novel concepts of radiation chemistry to commercial use.
So What Does Radiation Chemistry Have to Do With Heat Shrink Tubing?
Heat shrink tubing works because of the science behind cross-linked polymers. HST is composed of these cross-linked polymers as they link to form a three-dimensional network. When heat shrink tubing works properly it will conform and take the shape of the electrical wiring or the underlying connection splice.
What are the Main Functions of Heat Shrink Tubing?
When encountered in any other context, the weightless and seemingly trivial plastic tubing may not seem like anything to write home about. Yet, the science that makes the tubing possible has allowed for the protection and longevity of many important electrical systems, as well as binding loose wires, connectors, terminals, joints, and other electrical splices that make much of our essential services possible. The main functions of HST are:
-
Insulation: As mentioned above, electrical cables and connections should be insulated. These insulators should be composed of non-conducting materials that serve merely as a shield. The insulation helps conserve the energy and prevent it from dissipating. This shield helps protect the electrical innards from abrasion, sharp edges, or low impacts.
-
External protection: As well as insulating the wires, the tubing provides a shell of protection against environmental factors such as water, snow, wind, etc.
-
Organization: Large electrical setups tend to require a lot more than just a few wires. So when several electrical wires have to run in the same general area, the tubing helps to organize the wires.
-
Structural support: Strong tubing also serves a structural support role by allowing less strain on the wires and connectors.
New HST Technology Make an Engineers’ Life Easier
HST is an essential part of every electrical engineer’s toolbox. Today’s new technology of HST tubing manufacturing allows for stronger and more resilient tubing adaptable to varying conditions. Today’s manufacturers, for example, can use colorants to help with color coding and organization and UV protection to shield electrical setups from the harsh rays of the sun.
Find Quality Heat Resistant Tubing at HST Cable Management in El Paso
To protect your electrical setup and wiring, resilient heat shrink tubing should be part of your arsenal. HST Cable Management understands the essential role this tubing serves for many operations. Call us today and learn about the materials we have available for all your applications.